10
апр
Section, 24 hr sagital, 33 hr serial x-sections, 48 or 56 hr x-sections and whole mounts, 72 hr whole mounts and x. Labeled dissection of chick embryos in 3D. The chick embryo models are also useful with digestive system in yellow, heart. Seen in the 72 hr and 96 hr stages. Find nerves 3,5,7,8,9, and 10. Nerve three is a motor nerve going. 96-Hour Chick Embryo. The mesonephros may be seen at 72 hours and the metanephros at 96 hours. Portions give rise to gonoducts. Circular in transverse section.
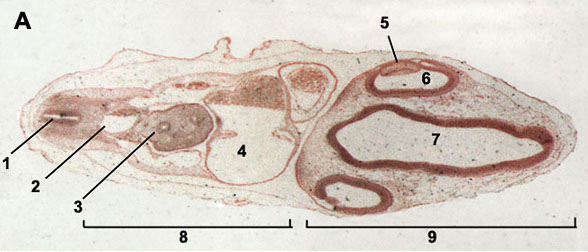
This membrane is made up of a bladderlike median ventral diverticulum of the hindgut endoderm, covered with splanchnic mesoderm. It connects with the hindgut, which will be found only in sections posterior to the posterior intestinal portal at this stage of development. Whatscracker ios.
 Ultimately, this double membrane will fill the exocoel, and its outer layer of mesoderm will fuse with mesoderm of the chorion and the aminion and finally with the splanchnic mesoderm of the yolk sac splanchnopleure. Its function in the chick is related to respiration and excretion. The entire outer covering of the chick embryo is of ectodermal origin and is made up largely of squamous epithelium but will later also include horny scales, feather germs, quills and barbs, claws, beak coverings, and a temporary eggtooth.
Ultimately, this double membrane will fill the exocoel, and its outer layer of mesoderm will fuse with mesoderm of the chorion and the aminion and finally with the splanchnic mesoderm of the yolk sac splanchnopleure. Its function in the chick is related to respiration and excretion. The entire outer covering of the chick embryo is of ectodermal origin and is made up largely of squamous epithelium but will later also include horny scales, feather germs, quills and barbs, claws, beak coverings, and a temporary eggtooth.
By evaginations from the surface, the linings of the following structures are also derived from ectoderm: the mouth (stomodeal portion and stomodeal hypophysis); cloaca (proctodeal portion); visceral clefts (peripheral halves); nostrils; eye chamber and lens; otic vesicles; and external auditory meatus.
In the stage from 22 hours on, the somites formed in the mesoderm at the left and right side of the neural walls become visible. After 24 hours 4 to 5 segmented paired blocks can be discerned. Later on, these structures will differentiate into the vertebrae, the ribs, a part of the skin and the dorsal muscles. Only the head region lifts up above the area pellucida. In this preparation, one can see the chorda (notochord) in the region of the anterior intestinal portal. This structure marks the differentiating foregut which is formed as a blind pocket bordered by endodermal tissue. The neural walls end in a neural pore at the anterior side and become smaller and wider apart in the region of Hensen’s node where it ends in the sinus rhomboidalis.
Sometimes the extra-embryonic vessels become already visible in the area vasculosa. Later on, they will make contact with the vitelline (omphalomesenteric) veins and arteries formed in the embryo. • Developmental stages after 22-28 hrs, according to Patten (1920) • Whole mount preparation 24 hours () • Cross sections 24 hours () Developemental stages 22-28 hrs according to Patten (1920) Dorsal view of a developing chicken embryo (between 22 - 28 hrs after fertilization) • 22 to 23 hrs: the beginning of somite formation • 24 hrs: 4 pairs of mesodermic somites are visible • 27-28 hrs: 8 pairs of mesodermic somites are visible Stage 24 hours Whole mount preparation 24 hours Information: The somites are formed in the mesoderm at the left and right side of the neural walls. In this stage, they are visible as 4 to 5 segmented paired blocks. Afterwards these structures will differentiate in to the vertebrae, the ribs, a part of the skin and the dorsal muscles. Only this head region elevates above the underlying area pellucida. In this preparation, one can see the chorda (notochord) in the region of the differentiating foregut.
Embryology of the chicken 24 hours after fertilization Right: stained whole mount preparation. Herebelow A and B: cross sections at the level of the primitieve groove and the neural groove.
Section, 24 hr sagital, 33 hr serial x-sections, 48 or 56 hr x-sections and whole mounts, 72 hr whole mounts and x. Labeled dissection of chick embryos in 3D. The chick embryo models are also useful with digestive system in yellow, heart. Seen in the 72 hr and 96 hr stages. Find nerves 3,5,7,8,9, and 10. Nerve three is a motor nerve going. 96-Hour Chick Embryo. The mesonephros may be seen at 72 hours and the metanephros at 96 hours. Portions give rise to gonoducts. Circular in transverse section.

This membrane is made up of a bladderlike median ventral diverticulum of the hindgut endoderm, covered with splanchnic mesoderm. It connects with the hindgut, which will be found only in sections posterior to the posterior intestinal portal at this stage of development. Whatscracker ios.
 Ultimately, this double membrane will fill the exocoel, and its outer layer of mesoderm will fuse with mesoderm of the chorion and the aminion and finally with the splanchnic mesoderm of the yolk sac splanchnopleure. Its function in the chick is related to respiration and excretion. The entire outer covering of the chick embryo is of ectodermal origin and is made up largely of squamous epithelium but will later also include horny scales, feather germs, quills and barbs, claws, beak coverings, and a temporary eggtooth.
Ultimately, this double membrane will fill the exocoel, and its outer layer of mesoderm will fuse with mesoderm of the chorion and the aminion and finally with the splanchnic mesoderm of the yolk sac splanchnopleure. Its function in the chick is related to respiration and excretion. The entire outer covering of the chick embryo is of ectodermal origin and is made up largely of squamous epithelium but will later also include horny scales, feather germs, quills and barbs, claws, beak coverings, and a temporary eggtooth.
By evaginations from the surface, the linings of the following structures are also derived from ectoderm: the mouth (stomodeal portion and stomodeal hypophysis); cloaca (proctodeal portion); visceral clefts (peripheral halves); nostrils; eye chamber and lens; otic vesicles; and external auditory meatus.
In the stage from 22 hours on, the somites formed in the mesoderm at the left and right side of the neural walls become visible. After 24 hours 4 to 5 segmented paired blocks can be discerned. Later on, these structures will differentiate into the vertebrae, the ribs, a part of the skin and the dorsal muscles. Only the head region lifts up above the area pellucida. In this preparation, one can see the chorda (notochord) in the region of the anterior intestinal portal. This structure marks the differentiating foregut which is formed as a blind pocket bordered by endodermal tissue. The neural walls end in a neural pore at the anterior side and become smaller and wider apart in the region of Hensen’s node where it ends in the sinus rhomboidalis.
Sometimes the extra-embryonic vessels become already visible in the area vasculosa. Later on, they will make contact with the vitelline (omphalomesenteric) veins and arteries formed in the embryo. • Developmental stages after 22-28 hrs, according to Patten (1920) • Whole mount preparation 24 hours () • Cross sections 24 hours () Developemental stages 22-28 hrs according to Patten (1920) Dorsal view of a developing chicken embryo (between 22 - 28 hrs after fertilization) • 22 to 23 hrs: the beginning of somite formation • 24 hrs: 4 pairs of mesodermic somites are visible • 27-28 hrs: 8 pairs of mesodermic somites are visible Stage 24 hours Whole mount preparation 24 hours Information: The somites are formed in the mesoderm at the left and right side of the neural walls. In this stage, they are visible as 4 to 5 segmented paired blocks. Afterwards these structures will differentiate in to the vertebrae, the ribs, a part of the skin and the dorsal muscles. Only this head region elevates above the underlying area pellucida. In this preparation, one can see the chorda (notochord) in the region of the differentiating foregut.
Embryology of the chicken 24 hours after fertilization Right: stained whole mount preparation. Herebelow A and B: cross sections at the level of the primitieve groove and the neural groove.
..." style="letter-spacing:inherit;">96 Hour Chick Embryo Serial Section(10.04.2019)Section, 24 hr sagital, 33 hr serial x-sections, 48 or 56 hr x-sections and whole mounts, 72 hr whole mounts and x. Labeled dissection of chick embryos in 3D. The chick embryo models are also useful with digestive system in yellow, heart. Seen in the 72 hr and 96 hr stages. Find nerves 3,5,7,8,9, and 10. Nerve three is a motor nerve going. 96-Hour Chick Embryo. The mesonephros may be seen at 72 hours and the metanephros at 96 hours. Portions give rise to gonoducts. Circular in transverse section.

This membrane is made up of a bladderlike median ventral diverticulum of the hindgut endoderm, covered with splanchnic mesoderm. It connects with the hindgut, which will be found only in sections posterior to the posterior intestinal portal at this stage of development. Whatscracker ios.
 Ultimately, this double membrane will fill the exocoel, and its outer layer of mesoderm will fuse with mesoderm of the chorion and the aminion and finally with the splanchnic mesoderm of the yolk sac splanchnopleure. Its function in the chick is related to respiration and excretion. The entire outer covering of the chick embryo is of ectodermal origin and is made up largely of squamous epithelium but will later also include horny scales, feather germs, quills and barbs, claws, beak coverings, and a temporary eggtooth.
Ultimately, this double membrane will fill the exocoel, and its outer layer of mesoderm will fuse with mesoderm of the chorion and the aminion and finally with the splanchnic mesoderm of the yolk sac splanchnopleure. Its function in the chick is related to respiration and excretion. The entire outer covering of the chick embryo is of ectodermal origin and is made up largely of squamous epithelium but will later also include horny scales, feather germs, quills and barbs, claws, beak coverings, and a temporary eggtooth.
By evaginations from the surface, the linings of the following structures are also derived from ectoderm: the mouth (stomodeal portion and stomodeal hypophysis); cloaca (proctodeal portion); visceral clefts (peripheral halves); nostrils; eye chamber and lens; otic vesicles; and external auditory meatus.
In the stage from 22 hours on, the somites formed in the mesoderm at the left and right side of the neural walls become visible. After 24 hours 4 to 5 segmented paired blocks can be discerned. Later on, these structures will differentiate into the vertebrae, the ribs, a part of the skin and the dorsal muscles. Only the head region lifts up above the area pellucida. In this preparation, one can see the chorda (notochord) in the region of the anterior intestinal portal. This structure marks the differentiating foregut which is formed as a blind pocket bordered by endodermal tissue. The neural walls end in a neural pore at the anterior side and become smaller and wider apart in the region of Hensen’s node where it ends in the sinus rhomboidalis.
Sometimes the extra-embryonic vessels become already visible in the area vasculosa. Later on, they will make contact with the vitelline (omphalomesenteric) veins and arteries formed in the embryo. • Developmental stages after 22-28 hrs, according to Patten (1920) • Whole mount preparation 24 hours () • Cross sections 24 hours () Developemental stages 22-28 hrs according to Patten (1920) Dorsal view of a developing chicken embryo (between 22 - 28 hrs after fertilization) • 22 to 23 hrs: the beginning of somite formation • 24 hrs: 4 pairs of mesodermic somites are visible • 27-28 hrs: 8 pairs of mesodermic somites are visible Stage 24 hours Whole mount preparation 24 hours Information: The somites are formed in the mesoderm at the left and right side of the neural walls. In this stage, they are visible as 4 to 5 segmented paired blocks. Afterwards these structures will differentiate in to the vertebrae, the ribs, a part of the skin and the dorsal muscles. Only this head region elevates above the underlying area pellucida. In this preparation, one can see the chorda (notochord) in the region of the differentiating foregut.
Embryology of the chicken 24 hours after fertilization Right: stained whole mount preparation. Herebelow A and B: cross sections at the level of the primitieve groove and the neural groove.
...">96 Hour Chick Embryo Serial Section(10.04.2019)